Light is a form of energy that is visible to the naked eye.
It is one of the most important resources for the survival of animals and plants on earth.
The applications of light include
- Photosynthesis
- Vision and sight
- Body growth and sleep
- Drying and evaporation
- Sanitation of Earth
- Temperature regulation
- In health care
- For communications and signal
- Electricity generation
- Microscopy
- Research
- Sterilization.
These bright rays were so fascinating for scientists like Albert Einstein.
Because, unlike other energies, it was visible, traveling at incredible speeds, and challenging to explain in scientific terms.
But with improvements in science and technology, light is explored for many benefits and applications, as below.
Benefits for Life
1. Photosynthesis for Food formation
- The energy from light is trapped as chemical energy and stored as food. As you might have known, this occurs through a process called photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis is a concept in biology wherein food is synthesized in green leaves in the presence of light.
- Light is the sole source of food generation for all living organisms.
- Except for a few chemotrophic bacteria? Almost all living beings depend on it for their food and energy.
- Plants and other autotrophs synthesize their own food materials through the use of light. When it falls on the leaves and other greenish surfaces, plants are trapped.
- This trapped energy is converted to reserve energy in the form of carbohydrates.
- Carbon dioxide and water are used up to form carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight. {CO2 +H2O= C6H12O6}

- Since plants are the first food chain source, all animals obtain their food from these plants.
- This phenomenon is observed both on the earth’s surface and also in marine environments.
So, light energy supplies food to all living beings on earth.
2. Uses of light in Vision and sight
- The human eye, those of other animals, can see the objects around them due to the presence of their eyes.
- But without light, these eyes might be of no use. The eyes receive the reflected images of the objects and send the information to the brain.
- From this visual information, we comprehend the objects. Hence, we can notice that in darkness, we cannot see anything.
- Further, it is responsible for Colors.
- This whole world looks beautiful due to its colors. But in darkness, we see no colors. This is because all the colors in this world are possible only due to light.
- The beam of light has many spectra. Each spectrum has a color and these are broadly referred to as VIBGYOR.
In full form, it is
- Violet,
- Indigo
- Blue
- Green
- Yellow
- Orange
- Red
- All these colors have different wavelengths and frequencies. And when light falls on an object, it absorbs some of the spectra and reflects others.
- The reflected rays fall onto our eyeballs and pass the impression to the brain, making it look colorful.
- So it is the ability of the object to absorb some spectra and reflect the remaining that makes it look colorful.
We would not see the color if the light is absent or our eyes are not functional.
3. Regulation of body growth, Sleep, and Body physiology
Exposure to the sun is essential for life as it helps to produce vitamin D, regulate sleep, helps in body growth, and more.
For Vitamin D synthesis

- Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is needed for bone health and immunity.
- This is synthesized in the body under the influence of sunlight. When we expose ourselves, Vitamin D is formed from ergosterol and cholesterol.
- When the rays fall on the skin, the ergosterol below the skin converts to vitamin D.
- So if someone stays away from sun exposure for a long time, he tends to develop vitamin D deficiency.
- Also, to get a regular dose of vitamin D, it is important to expose to the sun every day. The best time would be in the mornings and evenings (before dawn).
Sleep-wake cycle and circadian rhythm
- Have you noticed that you tend to fall asleep in the evening without knowing it is bedtime?
- Even you tend to wake up at sunrise without an alarm. This is due to the regulation of the body’s biological clock, which is associated with external time called the circadian rhythm.
- The pineal gland in the brain releases the hormone melatonin, which regulates these sleep-wake patterns.
- Similarly, everyday plants and animals are ticking with time.
- Plants broaden their leaves during the daytime, starting at sunrise. But with sunset, they stay low until next morning.
- Even the leaves and a few flowers like sunflowers, bend towards the light throughout the day.
- Animals like birds start chirping in the early morning hours and start to rest in the evenings when the light fades.
- The circadian clock (rhythm) inside plants and animals is responsible for such behavior, and this clock is influenced by light.

- Also, the plants grow in the direction of light as auxin, a plant growth hormone, is regulated by light.
- Birds, insects, and other animals are also controlled by light.
- We can notice birds stop making noises in the evening and start making noises early in the morning.
- This habit is controlled by light as it can tick their body clock.
- This light-dark cycle also influences body growth.
- Plants grow towards the sky as they are guided by light.
The plant growth hormone, “Auxin,” present in the tips, is responsible for the upward stem growth towards the sky.
Energy For body physiology
- As seen before, light energy is stored in food like carbohydrates.
- These are broken down in the body to produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- This ATP breaks down to ADP and AMP to release energy in the cells and tissues.
- This ATP is utilized for physiological processes like body movements, building the body proteins, generating heat in the body, etc.
- The cell and nucleus transcription mechanism uses this ATP energy to form messenger RNA (mRNA).
- This m-RNA, in the presence of ATP, again translates to producing desired hormones, enzymes, proteins, and fats required for the body.
- Thus, the light energy conserved in the food is used up to build and maintain its functions.
4. For Drying and evaporation
- Sunlight helps in the drying of soil, forests, air and rocky surfaces due to its ability to heat up.
- Also, it helps water evaporate from oceans and water ponds.
- This drying is helpful in two ways to live on earth, like
a) Water cycle
- The water cycle is how freshwater on the earth’s surface is recycled for drinking and irrigation.
- The water from the land evaporates to form clouds.
- These clouds again cause rainfall to return the freshwater to the earth’s surface.
- So due to rain, there is fresh water to drink and also use for irrigation.
Without the water cycle, all the water on earth would remain in the ocean so that no water is available to drink.
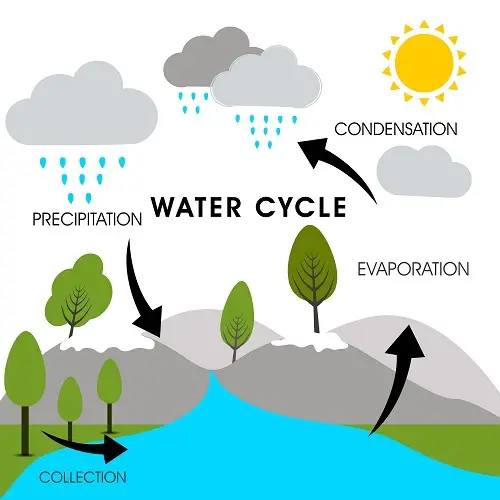
- Or, the water on the earth’s surface would be so filthy that it would be unfit for drinking.
- So sunlight contributes to the water cycle and maintains rainfall and water for human use.
5. For Sanitation and Scavenging
- Sunlight helps keep nature clean.
- Due to drying, weeds, algae, and other microbes do not grow, keeping the environment clean and tidy.
Even dead bodies and other waste materials get dried, lose their wet mass, and degrade fast.
6. Maintenance of temperature
- Light energy from the sun raises the temperature of the earth.
Due to this, life exists on earth.
- If you think so, why? Just imagine those areas of the earth without proper sun exposure for the whole year.
- Those areas are icy and even have heavy snowfall.
- If sunlight is absent, the earth’s temperature can drop drastically, such that the whole water on the earth gets frozen.
- The animals, especially homeotherms, die instantly due to low temperatures if this happens.
- Even poikilothermic animals may find it difficult to survive. So light is essential in maintaining temperature on the earth and thereby life.
Human Applications of this energy
1. In medicine
- In medicine, it is widely used as phototherapy.
- Exposure to light is preferred in treating newborn jaundice and skin conditions like psoriasis, mood disorders, and certain cancers.
2. For Communication
Data transmission
- Light is used to transmit data through optic fibers. Since it travels very fast, this technology is preferred for data transmission.
- It is used for broadcasting, telephone calls, computer networking, and medical diagnosis.
Signal system
- Light is the crucial visible signal. We use it as traffic signals, navigation signals, etc.

- Even our TV remotes use infrared rays to give the signal to Television.
- Thus, light appears to be a simple phenomenon of the universe with diverse uses for humans and life on earth.
3. Electricity generation
- Solar energy: Rays from the sun help to generate green energy or renewable energy.
- Solar panels imbibe sun rays and convert them into electric energy, which can be used for domestic needs.
- Now we have realized the importance of solar energy.
- It is one alternative energy or renewable energy, that is safe for the environment. It generates no pollution and other harmful wastes.

- Other means of energy generation by using coal and atomic energy are responsible for global warming.
So if we shift towards this form of energy, we will be saving the environment.
4. For Microscopy & Spectroscopy
Microscopy
- It is a technique used to observe minute objects invisible to the naked eye using a microscope.
- This technique needs light to help observe the image clearly under the lens.
- The microscope is also used to diagnose diseases using blood and sputum samples.
Spectroscopy
- Light is an electromagnetic spectrum and is used for the analysis of compounds by spectrophotometry.
- This spectroscopy can be used for both qualitative and quantitative analysis.
- Different spectroscopy methods vary based on the spectra and wavelength of light used.
- Some of them include colorimetry and atomic absorption spectroscopy.
This spectroscopy is further extended to be combined with other analytical techniques like chromatography.
5. For research in physics
- Light is widely used to study the properties of radiation.
- It is also used to study its properties and interaction with matter as a part of optical physics.
Light is also essential to observe objects in the universe for the Astronomers.
6. For Sterilization
- Light, especially its ultraviolet component, is an excellent sterilizing agent.
- Haven’t you noticed in a supermarket or hospital use of UV lamps?
- These UV lamps are good sterilizers. The UV rays kill the microbes in the air keeping the area sterile.
- So UV light is classified under the dry method of sterilization.
- Sunlight is an effective sterilizing agent.
When blankets and other hospital mattresses are dried in sunlight, all the microbes get killed and are relieved of bad odor.
Great article! We use light in our multiple day-to-day operations. However, it was never presented scientifically in such a way.
I am really grateful to the light energy and to the teachings of BRAHMAVIDYA for my spiritual enhancement, which teach me how I can increase the divine light in my body and make use of light for purification of my body and mind.
The information you gave was very helpful !!! Thanks to you I can finish my project about light.
Amazing I have to write 5 paragraphs about light this was really helpful
why light is seen before the sound of thunderstorm is heard when rain storm occurred.
The speed of Light travel is very much greater than the speed of the sound.Hence, we see light first during lightening as it travels fast to our eyes. While, the sound travels slower and we hear it latter.
Very good????????????????
Why is light important in film and television production?
Very interesting
wow that was a helpful use and now im in trouble for learning
Nice information of Sterilization
Thank you
Such good advice
Thanks that was so interesting
Oops like Robbin, it is votal info for my sermon.
Very informative for use in my Bible study of, “You are the light of the world.” I had to list all the benefits and effects of light.
Thank God for providing the light. Its awesome!
Nice and useful for me. thank you so much.
what is some light things we use today
Enlighting found out how much we use light without realising it.
Very helpful,thanks.
it was very nice