Blood is a vital substance in the human body.
It is a type of liquid tissue which helps to spread substances from one place to another in the body.
It is mainly composed of water, blood cells and other elements and substances.
It has many functions in the body and some of these functions are carried out by blood cells.
But unlike normal body cells, blood cells are entirely different in being isolated from each other (not packed to form a tissue, free moving).
Blood cells perform many functions and almost all the components are involved in some or other individual function.
The blood cells are formed by different tissues like bone marrow, lymph glands, etc.
Types of Blood cells
They are broadly three types of blood cells like
1. Red blood cells (R.B.C) / Red blood corpuscles
2. White blood cells
3. Platelets/ thrombocytes
Red blood cells: These are cells responsible for the reddish color of the blood. They are very high in concentration to other blood cells. There are approximately 5 million cells per microliter in males and 4.5 million in females. These cells are devoid of the nucleus, mitochondria and other cell organelles so termed as corpuscles.
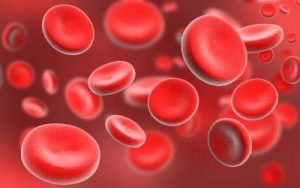
As seen in pic, they are red with a biconcave shape. They have a pigment called hemoglobin which is a complex of Heme (+iron) and globin= a porphyrin protein. This pigment is responsible for its red color and its oxygen carrying capacity. Thus R.B.C are involved in the transport of oxygen from lungs to the tissues. When the blood reaches the lungs, these RBC’s take up oxygen from the air. When they reach tissues by blood flow, there they give away oxygen due to the concentration gradient. The CO2 from tissues is dissolved in the water content of the blood and expelled from the lungs. Thus RBC vital function is to carry oxygen in the body to every tissue.
When the RBC’s are low or hemoglobin inside is low, it results in anemia.
They are formed in the red bone marrow of long bones in the body. Their life span is 120 days. After the lifespan, they are destroyed in the liver and spleen by reticulo endothelium.
White blood cells:
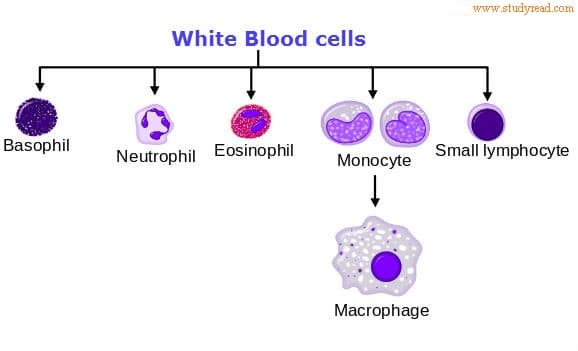
These are the cells which white in color and hence also called leukocytes. They are about 4.5 to 10.5 x 10³ cell per micro-liter of blood. These cells unlike RBC’s have a prominent nucleus and other cell organelles. There are six types of white blood cells like polymorphonuclear neutrophils, polymorphonuclear eosinophils, polymorphonuclear basophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, and a few plasma cells. The first three types are categorized as granulocytes and the next as agranulocytes.
Granulocyte type of leukocytes viz. as basophils, acidophils, neutrophils are named because of their nature to get stained by basic, acidic and neutral dyes respectively view under a microscope. They have a nucleus which of different shapes hence polymorphic. Further, under the microscope, there appear some granules in the cell body. Hence the name granulocytes.
Agranulocytes include lymphocytes and monocytes. These agranulocytes have a cell body which is nongranular in appearance hence the name non-granular or A+ granular.
Granulocytes and monocytes are involved in body defense against foreign substance or organisms like bacteria inside the body by engulfing them, i.e., by phagocytosis. They are mainly engaged in defense of the body from pathogens and injury.
Their defense is by two types. i.e., production of antibodies to neutralize the pathogenic antigen and the other form is engulfment of the pathogen. These cells are deprived in number in the condition like an infection.
Further, in case of infection, they are concentrated at the site of injury or inflammation to assist faster repair of body tissue.
Lymphocytes are involved in the immune component of the body immunity against the disease.
Their concentration ranges around 7000 cells/microliter of blood. Their decline indicates infection or pathological condition. Their rise in number is also seen in infection or the region of the body infected. Their abnormal rise in number is a condition of leucocythemia is, i.e., a blood cancer.
Their life span is a few hours like 4-5 hours in circulation and five days in the body region of infection or repair.
Their normal count is
Neutrophils count is 2-7.5 x 103
Basophils Count is 0-0.2x 103/mcl
Eosinophils count is 0.1-0.5 x10³/mcl
Lymphocytes count is 1.5-4 x 10³/mcl
Monocytes count is 0.2-1 x 10³/mcl
Check out more details on the type of white blood cells and also the difference between red and white cells.
Platelets/ thrombocytes: They are spindle-shaped cells in the blood. They are approximately 150 to 450 x 10³ per micro-liter of blood. They have clotting factors in them and also serotonin. Hence they are involved in the formation of blood clot.
Their decline in blood is called thrombocytopenia. This can leads to bleeding disorders namely hemophilia etc.
Their increase is seen in inflammatory diseases, while their decline is seen in diseases like dengue.
Besides the above differences, there is a difference in blood groups and rho factor. You may read about negative blood groups for more.
Nice
awesome. well written.
Thanks for the complement pinky..