The plants are the important components of this living ecosystem. Their life cycle starts with the falling of seeds on the ground, dispersed by some pollinating agents.
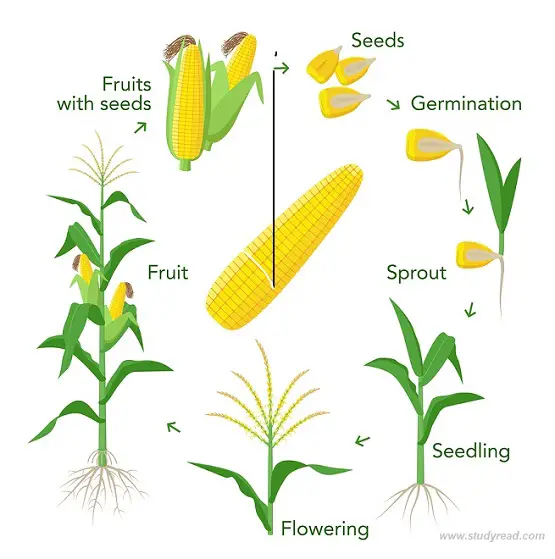
The 6 stages of the plant life cycle
- Seed stage
- Germination
- Growth
- Flowering stage
- Pollination (Reproductive stage)
- Fruit stage (Seed dispersal stage)
Generally, the life cycle of the plant is a simple one with fewer complications.
There are various plant life cycles, but the more advanced and mainly studied one is –the angiosperms (flowering plant) life cycle.
The stages of the plant life cycle
Seed stage
- This is the first stage of the life cycle in plants.
- The seed contains a miniature plant inside it in the form of an embryo.
- In angiosperms, the cotyledons are also found, which provide nourishment to the growing embryo inside the seed.
- The seed gets dispersed by various agents to distant soil where the development occurs.
- Cotyledons emerge as the first leaf after the germination of the seed.
- The seed coat is the additional coverage that protects against the harsh conditions of the environment.
Germination
- As the seed falls on the ground, the seed needs a suitable temperature and moisture to start the germination process.
- After the seeds are planted in the soil, under suitable conditions, the seed starts absorbing moisture and water, resulting in the swelling of the seed.
- This swelling leads to the rupture of the seed coat, and the hypocotyl emerges out of the seed to transform into the stem.
- This proliferation of a little stem-like structure from the seed is called germination.
- In monocots, the seed coat does not rupture and is fixed in one place.
- The hypocotyl originates from one specific point in the monocots.
- After this, the tiny root also grows downwards into the soil.
- This root helps absorb water and other nutrients for the growth and development of the plant.
- After this, the last stage of germination witnesses the shredding of cotyledons which culminates in to form the new leaves.
Growth stage
- In order to sustain the various developmental changes in its body, the plant produces food.
- This food is produced by the process of photosynthesis and is essential to the growth life cycle.
- The process of photosynthesis occurs by adding up carbon dioxide and water to form glucose and release oxygen.
- The chloroplasts in the leaf cells help in the process by trapping the sunlight. This light energy is used for the hydrolysis of water.
- The sugars that are produced by photosynthesis get stored in the roots and stem.
- The plant’s root system develops further and anchors the soil firmly to give the proper support to the plant.
- The meristem tissue in the leaf divides and proliferates into new leaves.
- After a while, the adult plant gives out the flowers on the stem, which marks the next stage in the life cycle of plants.
Pollination stage
- Pollination is a stage where the plants release pollen grains to reach the female part of the flowers.
- Some of the flowers may contain only the male or the female parts and not both.
- In such a case, the pollen is carried away from one flower to another with the help of the pollinating agents.
- This results in the pollen distribution onto the female part’s stigma.
- The pollinating agents are mainly the wind, water, birds, or some insects like honeybees.
- These pollinators play an essential role in producing new species of plants.
- Even when the flower is bisexual, the plant benefits from the other flower’s pollen.
Reproduction stage
- The flower is the sexually reproductive part of the mature plant. The complete flower forms within the early bud on the stem.
- The petals of the flower are variously colored to attract the pollinating agents.
- The female part of the flower is called the pistil, which includes the stigma, style, ovary, and ovules.
- The male part is called the stamen, which consists of a long filament called Anther, where the pollen matures.
- The pollen is disbursed onto the stigma of the female part, where the pollen gets attached to its base.
- As the pollen gets trapped, it traverses the style to the ovary.
- The eggs in the ovary get fertilized with pollen.
- The fertilized eggs take the form of seed, and the ovary develops into fruit by shredding off the flower components.
Seed dispersal stage
- Seed dispersal is the final stage of the plant’s life cycle.
- The seeds separate from the parent plant and are spread in the atmosphere by wind, animals, or the water current.
- The seeds get dispersed to distant positions where they eventually start the plant’s life cycle in new soil.
The above events continue to occur with the seeds dispersed in the land.
Frequently asked questions and answers.
-
What structures or stages in the life cycle of a plant are haploid
Pollen and ova are haploid in nature and they exist in the pollen stage and reproduction stage.
-
When does meiosis occur in the plant life cycle?
It occurs during the flowering stage or pollen stage.
-
Which part of the plant life cycle does pollen grain represent
Pollen grain represents the flowering stage of the plant.
References:
- Plant Life Cycles by Julie Lundgren
- Parts of a flower