The human body has different organs located in various parts of the body. These organs work together to form 11 human body systems that play a vital role in body physiology.
The organ systems include
- Skeletal system
- Muscular system
- Respiratory system
- Cardiovascular system (Circulatory system)
- Digestive system
- Nervous system
- Endocrine system
- Reproductive system
- Urinary system
- The lymphatic system (Humeral system)
- Integumentary system
An organ is formed by a group of tissues. These tissues are, in turn, formed from a group of cells.
A group of organs working together towards a common goal is classified as an organ system.
Details on Body Systems with Functions
1. Skeletal system
- This system consists of the bones of the body.
- These bones are made of bone cells and cartilage cells, which are hardened.

- They provide the body with a proper shape, frame, and support for the organs.
- In some places, they form bony compartments.
- These compartments include the skull and thorax, eye sockets, etc., which protect the essential organs like the brain, heart, lungs, and eyes.
- The skeletal system is also flexible and movable at places called joints.
- These joints help in the body’s movements and coordination with skeletal muscles.
2. Muscular system
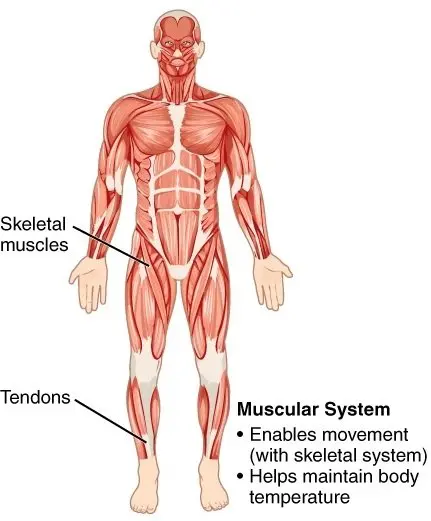
- This system comprises muscles that are responsible for the movements of the body.
- They are of three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles.
- Skeletal muscles help in moving the body from one place to another. Functions like walking, running, moving, lifting, and bending are possible due to skeletal muscles.
- On the other hand, the cardiac muscles form the heart and help pump blood. It forces the blood to flow through the arteries to reach the deep and remote areas of the body.
- Meanwhile, smooth muscles are present in organs such as the stomach, intestine, uterus, and urinary bladder.
- These smooth muscles bring about movement within the body to aid physiology.
3. Respiratory system
- The respiratory system helps in gaseous exchange.
- It helps absorb the atmospheric oxygen from the air and supply it to the body, leaving out carbon dioxide from the body and releasing it into the air.
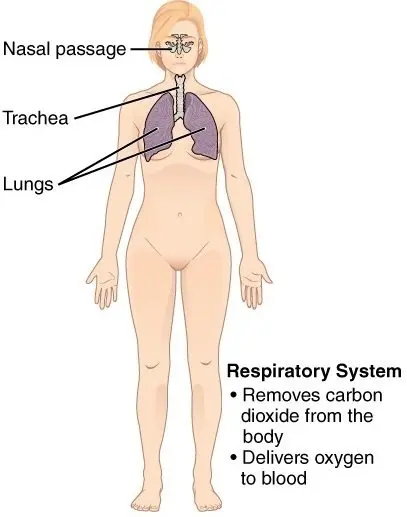
- The respiratory system comprises the organs like the nose, larynx, bronchi, and lungs.
- The path is called the respiratory tract, and a diaphragm made of skeletal muscle separates it from the abdomen.
- The oxygen is absorbed into the blood from the lung alveoli and carried to tissues. In the tissues and cells, it helps to generate energy through the oxidation of glucose in the mitochondria.
- Besides, the respiratory system also helps in speech (making sounds), excretion by exhalation (alcohol), and metabolism.
4. Cardiovascular system
- The cardiovascular system circulates the blood in the body.
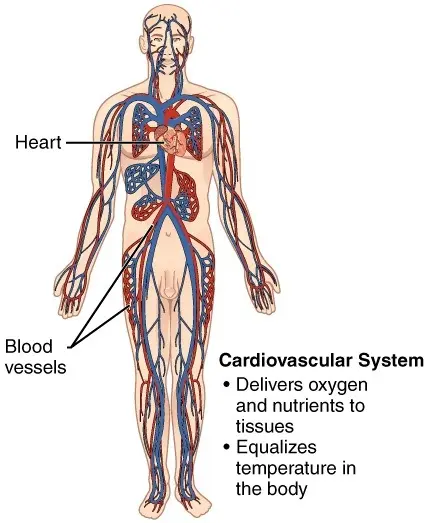
- It comprises blood and blood vessels like the arteries, veins, capillaries, and heart.
The main functions of this system are
- Maintenance of uniform temperature,
- Supply of oxygen and nutrition to all the cells and tissues
- Waste matter is collected and transported to the urinary system.
- To carry hormones to the target organs.
5. Digestive system
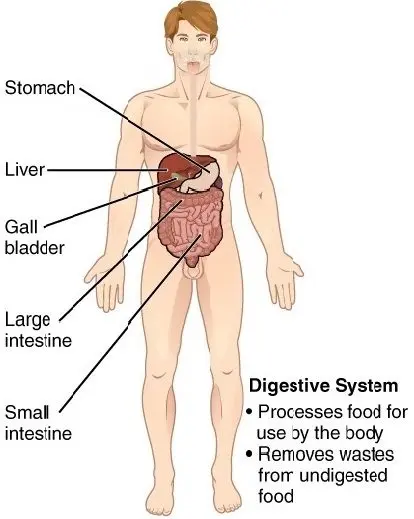
- This system is meant to break down the food and absorb nutrients into the blood circulation.
- It consists of the mouth, teeth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, intestine, rectum, and anus.
- It is the only route through which the food can enter the body.
- The food is broken down into smaller forms like carbohydrates, amino acids, and fatty acids for easy absorption into the body.
6. Nervous system
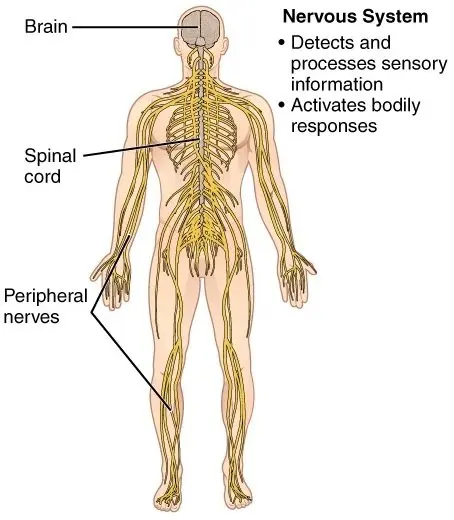
- This is called the master body system, as it controls all the other organ systems of the body.
- The nervous system regulates whole-body physiology, functions, and movements.
- It has a brain, spinal cord, and somatic and autonomic nerves (sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems).
- It stimulates the release of hormones when needed to control other systems.
- It regulates body movements through muscles and controls respiration, heartbeat, digestion, urination, etc.
7. Endocrine system
- This system acts as complementary to the nervous system.
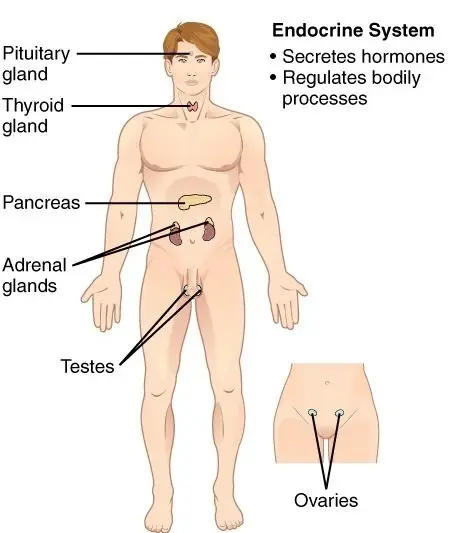
- Endocrine glands like the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, pineal, adrenal glands, testes, and ovaries are present in this system.
- The glands secrete their specific hormones, which act on different systems of the body and induce changes. These hormones are chemical messengers.
- For example, melatonin, a pineal gland hormone, induces sleep at night.
- There are different hormones controlling specific physiological processes.
8. Reproductive system
- This is the organ system that is responsible for the continuation of species.
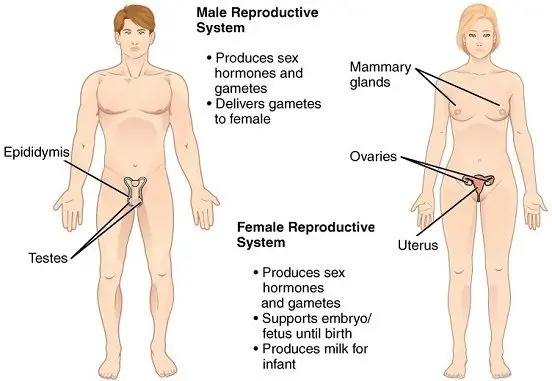
- It helps in the formation of offspring to keep up further life.
- In males, it comprises organs like the testis, penis, and prostate glands.
- In females, it consists of the vagina, uterus, uterine tubes, ovaries, and also mammary glands (breast).
- This system is quite interesting in that it is just one set and depends on the opposite sex for its important physiological process.
9. Lymphatic system
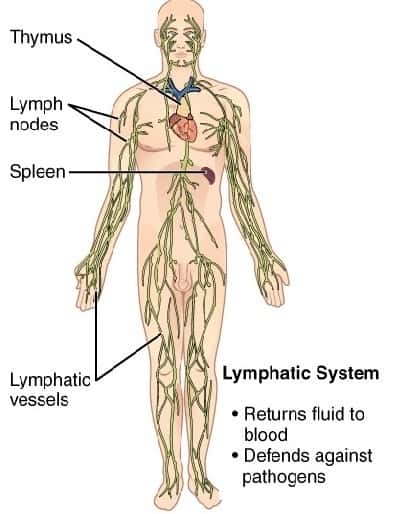
- This system provides a natural defense for the body. It kills bacteria, viruses, and other parasites residing in the body.
- It comprises fluid lymph, lymph nodes, lymph organs (like the spleen, tonsils, and thymus), white blood cells, and antibodies (humeral substances).
- The lymphatic system is arranged parallel to the blood circulation and widely distributed in important body points.
- You can find it in the intestine, kidney, liver, brain, etc., where it traps the pathogens and prevents their further spread by destroying them.
10. Urinary system
- This system, as the name indicates, forms the urine as its end product.
- It is meant to remove the wastes and other toxins from the body.
- This system has a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, one urinary bladder, and a urethra.
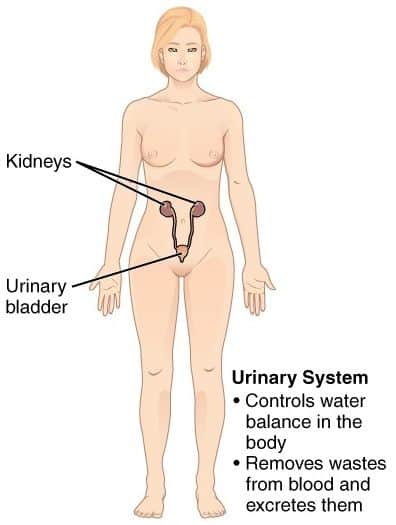
- Any substance in the body is converted to a water-soluble form by metabolism.
- The blood transports this to the kidneys.
- When the blood flows through the nephron in the kidneys, it gets filtered to release those wastes.
- This waste with water is called urine and is expelled from the body by urination.
- The load on the kidney is reduced as other organs like the skin, lungs, and saliva also participate in the excretion of waste from the body.
11. Integumentary system
- This is a covering system that covers the whole body surface.
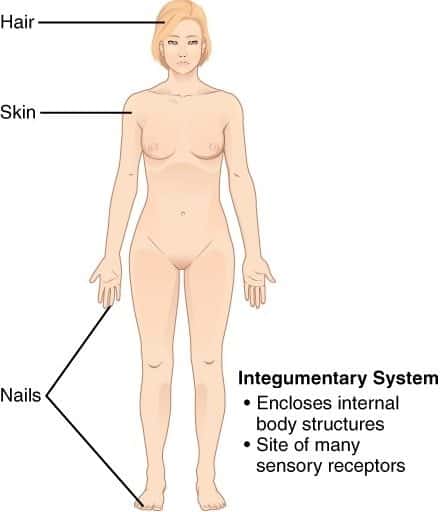
- The organs under this system are skin, hair, nails, etc.
- It prevents dehydration and heat loss.
- It also keeps the body safe from damage, wear, and infections.
Thus, from the above, it is clear that the body has different organs and organ systems.
They are all interconnected and collaborate in functions.
So, if one system is affected, other systems are also affected and cease to function.
For example, the digestive system is an organ system comprising organs like the stomach, esophagus, buccal-cavity, intestine, rectum, pancreas, liver, etc.
All these organs are concerned with one important physiological function, namely digestion.
If one of these organs is disturbed, then the whole digestive function is disturbed.
So, these organs are perfectly interlinked and connected to effectively carry out one specific physiological function.
In most cases, every organ in the organ system has only one specific physiologic function.
However, some organs may be a part of one or more organ systems.
For example, the pancreas is a part of the digestive system but also plays a prominent role in the endocrine system.
This is because it secretes digestive enzymes through its exocrine glands and insulin-like hormones through its endocrine portion.
The organ systems are similar in terms of function and anatomy, starting from amphibians to higher animals. The different organ systems in the human body include.
Frequently asked questions and answers.
What organ systems work together?
Organ systems like the nervous system and endocrine systems, circulatory and urinary systems, and skeletal and muscular systems work together.
Which organ systems contain the eye?
The eye can be placed in the nervous system as it is located in the brain compartment and is also mainly made of nerves.
What body systems work together to maintain blood pressure?
The nervous system, circulatory system, and urinary system maintain blood pressure.
What organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis?
The nervous system and endocrine systems maintain homeostasis. The nervous system detects changes and gives out impulses by regulating hormone release.
Which organ systems work together to release energy from food
The systems involved in the release of energy from food include the digestive system, which breaks down the food; the respiratory system, which supplies oxygen for oxidative phosphorylation; and the circulatory system, which carries the digested food and oxygen to the cells and tissues where energy is released.
Which two organ systems work together to inhale oxygen
The nervous and respiratory systems are mainly involved.
The respiratory center in the brain triggers inhalation by the lungs. At the same time, lungs take in air.
What 2 body systems work together to help you move
This would be the skeletal system and the muscular system.
What system protects the underlying organs from drying out
The circulatory system, in coordination with the nervous system, protects the underlying organs from drying out.
Which system gets rid of unwanted waste
Unwanted waste is removed by a combined work of two or three systems like
1. Urinary system
2. Circulatory system
3. Digestive system (liver and gut)
👉 Urinary system helps to clear the waste from blood.
👉 Liver converts the water insoluble waste into water soluble forms so that they can be removed by urine.
👉 The circulatory system helps transport the waste to the excretory organs from all over the body.
Please in all your articles, give the author's names. Thankyou
Hi William, updated as per your advice.
thank you for sharing. very informative.
not really
Hi,
This summer I made a great discovery. For more than one year I suffered of urinary urgencies with severe burning. I sort foods with little result. Sugar was the worst. I accused bread, milk, sweet fruits, salt, pickles, and so on. I considered normal at my 75 age. I had an inguinal hernia surgery and I accused that for my urinary tract irritation and urine produced burnings, especially the muscle responsible to prevent urine from leaving the bladder. I used dippers. I also consider to have sun-bathing this summer for vitamin D.
I live in Washington state so here is not warm enough to stay in sun. Years ago, I bought a land in Nevada near the city Winnemucca, where the temperature is 96 F and I can stay in sun without to experience cyclic vomiting syndrome.
For more than one year I used to eat sausages and bologna turkey. I noticed some itching infection on my chest and legs. During my travel to Nevada 700 miles, I eat just those foods. Once on my land I discovered on my chest another spot of infection with white heads. The conclusion was obvious, the foods I eat are responsible. I did not eat that kind of meat. After 4 weeks of staying in sun my chest become clean and no more itching on my chest and legs. Now I am back in Washington and I can eat bread, milk, gem, donuts and no more that urinary urgencies and no more dippers.
I also use warm clothes to prevent and cure infections. I feel great.
Please let people to know my discovery.
if someone is interested write on my email davidmuresan@live.com
David Muresan