Mitochondria are the cell organelles that produce energy.
They are the places where the tri-carboxylic acid cycle occurs, leading to a complete breakdown of glucose into water and carbon dioxide.
In doing so, they produce energy by oxidative phosphorylation.
A cell cannot survive without mitochondria. Hence mitochondria are present in both plant and animal cells.
Mitochondria are small sac-like structures floating in the cell.
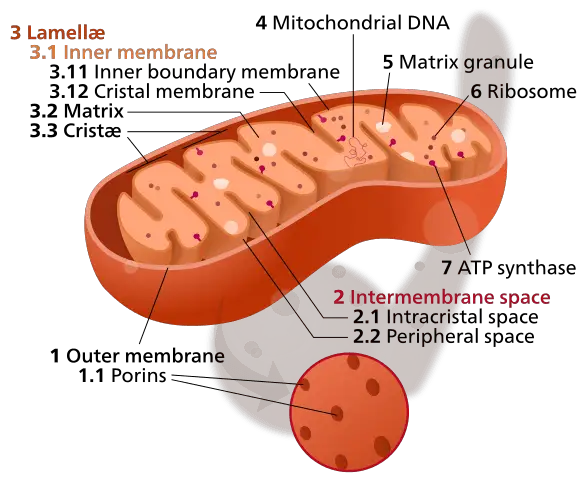
Below are some interesting facts on mitochondria. But before you go through it, kindly refer to the information regarding the structure and function of mitochondria if you are not aware of in the video below.
Mitochondria Facts in cell
1. Mitochondrial fusion
- As per Karen hales, a faculty of Davidson College-North Carolina, Mitochondria fusion is a process where mitochondria constantly fuse (merge) and divide to form tubular networks.
- The process involves the physical merging of both the outer and inner membranes of mitochondria.

- This network formation is a dynamic process meant to maintain the health of the cell.
- This process is especially active in stressful conditions to overcome genetic malfunction.
- Fusion activity leads to elongated mitochondria, while fission activity leads to fragmentation.
- This is an interesting concept on how cell survives stress through dynamics of mitochondria.
2. Single-stranded DNA & ribosomes
- They have their own cDNA, which is single-stranded.
- They can multiply on their own without the involvement of the cell division.

- Mutations in mtDNA can cause some diseases like myopathies, diabetes mellitus, neurological disorders, etc.
- Also, mitochondria have separate ribosomes, which are also different in size than normal ribosomes present near the nucleus.
3. Semi-autonomous organelles
- Mitochondria are semi-autonomous organelles due to the presence of DNA and their own ribosomes.
- They can multiply on their own and also form required proteins without the involvement of the nucleus.
4. Complex enzymes
- The matrix of mitochondria has four complex enzymes that help in its function. These complex-enzymes include
Complex-I is a combination of NADH-Q-Reductase. It contributes to translocating protons across membranes.
Complex-II is a combination of Succinate-Q-Reductase made of two polypeptides.

Complex-III is QH2-Cytochrome-C-reductase.
Complex-IV is Cytochrome-C-Oxidase.
These complex enzymes help in the generation of ATP, which acts as energy for the cell. This ATP production involves the coupling of oxidative phosphorylation.
5. Cell death
- They are also essential to cell organelles involved in cell death.
- They initiate programmed cell death by a process called apoptosis. See the role of mitochondria in cell death.
6. Number of mitochondria per cell
- Liver cells contain approximately 1600 mitochondria, while kidney cells have 1000 mitochondria, while some oocytes around 300000 mitochondria.
7. Structural changes
- Though mitochondria of different cells are similar in an animal, they vary slightly in structure.
- The skin cell’s mitochondria, which have less folding in the inner membrane to form cristae.
- While those in muscle cell have more folding to form more cristae, the more the cristae, the higher is the respiratory capacity and the energy generation.
Mitochondria in diseases
8. Mitochondrial drugs and diseases
- Defects in mitochondria can lead to a few diseases.
And hence drugs are being developed which target mitochondria for the treatment of diseases.
9. Death by poisons
- Many poisons like cyanide cause death due to their action on mitochondrial enzymes.
- Poisons like Cyanide, heavy metals inhibit the function of complexes within the mitochondria, leading to animals’ instant death.
10. Isolation for experiments
- Though they are very minute in size, they can be isolated for testing and diagnosis in labs.
- Their specific gravity is more than the cytoplasm. Hence they can be isolated from cells and tissue homogenates by ultra-centrifugation.
- They can be observed under the microscope by staining with Janus green. Darkfield illumination with phase-contrast setting helps in viewing them.
- Also, the number of mitochondria varies between plants and animals. Plant cells have fewer mitochondria than animals cell.
Frequently asked questions and answers
Why do some cells have more mitochondria give an example
Mitochondria are present in large numbers in cells that require a high amount of energy. These cells include nerve cells, skeletal muscle cells, and liver cells (hepatocytes)
What chemical reaction happens in mitochondria
As a part of the TCA cycle, oxidative phosphorylation occurs.
How are mitochondria adapted for respiration?
Mitochondria have the machinery to perform oxidative phosphorylation. It means it promotes phosphorylation by oxidation of substances leading to the formation of ATP
Why do liver cells have large numbers of mitochondria
The liver is the seat of metabolism in our body. Here many chemical reactions occur requiring large amounts of energy. Hence, the liver cells have more mitochondria to facilitate the process.
References:
Great, interesting article.
Thanks for it!
..this indeed clearly pictures how it’s working ,well written and pictures are indeed good ..