Beneficial Bacteria definition
These are the bacteria that are helpful to other living organisms through the way of nutrition, health, or any other support without causing any harmful effects.
Bacteria are viewed projected as they are very harmful to humans. But in fact, they have a very great role in human life, ecological stability, and the environment.
Bacteria are the most robust unicellular microorganisms.
They can survive even in adverse conditions like extreme temperatures (high or low), starvation, droughts, etc.
They can do this because of their ability to reproduce faster and transform into metabolically inert yet live forms.
These inert forms are called spores, which rupture to give out bacteria when suitable conditions arise. Bacteria are a boon to the environment, and without them, the surroundings around us could not have been clean and tidy.
They are also of vital importance to humans, plants, and animals.
They contribute to human health in terms of body physiology, metabolism, and excretion.
Beneficial bacteria for the environment
♠ Natural scavengers
Bacteria are the natural scavengers on the earth. They decay any dead and waste matter on the surface of the earth and in the soil.
Hence there is no accumulation of corpses of animals over so many years of the emergence of life on earth.
These degraded and decomposed substances add to the fertility of plants or convert to biogas.
♠ Further, they degrade any chemical or biochemical fallen on the soil and thereby detoxify the valuable soil.
Thus they make it fit for the growth of plants & animal-safe survival on the earth.
Even a vast amount of chemical and other waste is degraded over weeks in the water.
Or else the soil and water would be toxic for further use.
♠ Nutrition
They are an important source of vegetative nutrition in the marine environment.
They provide major & micro-nutrients required for the sustenance of marine animals as they form the starting point of the marine food chain.
Benefits of bacteria for plants
As a source of manure (fertilizer enhancers).
♦ Bacteria are helpful for plants. They render the soil suitable for the growth of plants.
They break down any dead and organic matter into humus so that the plants receive essential mineral elements for growth.
♦ Ammonifying bacteria that convert proteins, amino acids, and nucleic acids of dead bodies into ammonia. Ex: Bacillus.

♦ Nitrifying bacteria: Ammonia is also oxidized to nitrates by nitrifying bacteria. Ex: Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter.
♦ Similarly, phosphate solubilizing bacteria help convert inorganic phosphate into a soluble form such that they can be absorbed by plant roots.
Benefits of bacteria to humans and animals
- Bacteria like Entero-coli live in the gut intestines of animals in a symbiotic fashion.
They are friendly bacteria helping in the degradation of unused food and help in its expulsion from the body.
- Bacteria like E.coli, which are present in the body, resist the growth of harmful bacteria like typhoid.
These human-friendly bacteria help in the production of Vitamin-K in the intestine.
They also keep a check on the growth of harmful bacteria. Without them, the body would be susceptible to harmful infection.
Hence, when we use antibiotics irrationally, these good bacteria are killed, leading to secondary infections by pathogenic bacteria.
Medical benefits of bacteria
Bacteria are also useful for medicine as they help in the production of drugs for treatment.
For antibiotic production
Antibiotics are produced by bacteria and other microbes like fungi.
These antibiotics could rescue people from other harmful and pathogenic bacteria.
Initially, most antibiotics were produced by fermenting large cultures of bacteria. Now synthetic ones are in large supply.
For the production of vaccines
Bacteria are used to produce vaccines by either separating their antigens or sometimes dead form or else even living ones with a lack of pathogenic character.
Ex: TB vaccine is one where dead bacteria of TB are administered to build up resistance to tuberculosis in humans. Once administered, these bacteria cannot cause disease. But the body will be able to produce antibodies to kill any infection of Mycobacterium.
Probiotics
Bacteria are also used as part of probiotics. These are friendly bacteria that can be used to fight infections. They are specially used to treat diarrhea in children.
For genetic engineering
Bacteria have short reproduction cycles. Some of them can divide in the minutest o produce new daughter cells. This factor of bacteria is used in biotechnology to produce biological compounds. Products like insulin, vitamin B12, etc., are supplied on a large scale on a continuous basis due to their manufacture using genetically modified bacterial cells.
For an idea, check → rDNA technology applications.
Importance of bacteria in agriculture
Bacteria play a vital role in agriculture for disease prevention and enhancing fertility.
1. Bio-pesticides
They act as bio-pesticides to kill disease-causing diseases in crops and aid in higher yield.
Ex: Bacillus thuringiensis is one example of a pesticide to kill pests. Some species of Bacillus and Pseudomonas act as antifungals.
These bacteria are such that when applied, they kill only the disease-causing pests and insects.
But they do not harm the plant or farmer because they are specifically harmful to pests.
Composting is a way to make natural manure. This manure imparts fertility to the soil.
Further, they are not harmful to the soil, unlike chemical fertilizers.
Chemical fertilizers pollute the soil, air, and water around them. But the use of biopesticides avoids this problem. Further, they are less expensive.
2. Organic manure
Some farmers even make their own organic compost by using kitchen and other vegetable waste.
This waste is allowed to decompose in the presence of moisture, air, carbon, and nitrogen ingredients.
Check out organic composting.
3. Biofertilizers
When bacteria like blue-green algae are left in agricultural soil, they fix natural manure in the form of nitrogen from the air to enter the growth and yield of crops.
Also, when a crop is harvested, the plant remains are allowed to degrade in the soil.
Under rainfall, this waste material is acted on by bacteria to decompose it.
This organic material acts to increase the water retention capacity of the soil.
Further, organic waste acts as natural manure and gives essential nutrients to the next crop.
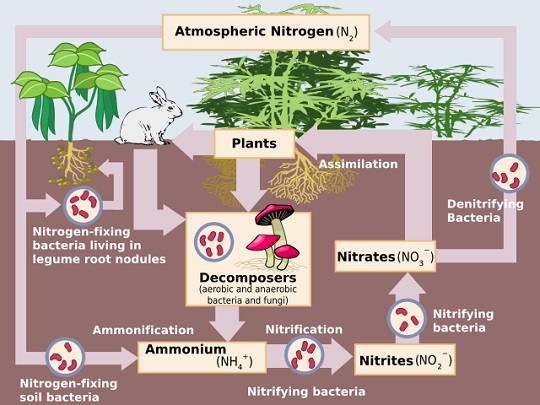
Further, these bacteria play a role in nitrogen fixation.
Importance of Bacteria in the nitrogen cycle
1. Fix nitrogen in the soil
Bacteria like chlorella are used as green manures to increase soil fertility. There absorb nitrogen from the air and fix it in the soil.
Thus the nitrogen content of the soil increase and provides fertility to crops. Ex: cyanobacteria.
Hence, these are beneficial bacteria for soil as they help
2. Crop rotation
Farmers cannot grow the same crop year after year.
If they do so, the yield of crops drops, and also the subsequent crops are affected by pests and diseases.
To avoid this, the farmers opt for crop rotation. This crop rotation is done by alternating crops with a leguminous crop.
For example, a farmer growing cotton this year will opt for a leguminous crop like groundnut or peanut next year.
This not only destroys the pests of the previous crop but also builds fertility.
This rise in infertility due to leguminous crop is due to the presence of symbiotic bacteria in the roots.
Rhizobium is an example of such bacteria.
These bacteria reside in the nodes of the roots of leguminous plants and help absorb nitrogen from the air and fix it in the roots.
In turn, these bacteria extract nutrition from the plant (symbiosis). Thus bacteria help the plant and also build fertility in the soil.
Importance of bacteria for industry
Bacteria are also useful for industrial & commercial purposes.
♠ Fiber industry
Bacteria like clostridium butyrcum is used in the retting of flax and sunn hemp to extract the clear fiber.
♠ Tea and tobacco
Micrococcus and Bacillus megatherium are used in the curing of tea and tobacco.
♠ For the beverage industry
For this industry, bacteria contribute to the fermentation of wine used as beverages to form alcohol.
♠ Dairy industry
In the dairy industry and homes, ferments milk to produce a curd.
♠ Sterilization
This is a process to eradicate microbial contamination from finished products.
Few bacteria are used as biological indicators for sterilization validation.
These bacteria are available commercially as strips containing spores.

The economic importance of bacteria
Bacteria are sold in different forms for use, as seen before, like
a. Medicine (probiotics), antibiotics, insulin, and other medicines are obtained from them.
b. Agriculture as bio-pesticides and fertilizers. In fact, this is a big industry and makes a lot of money.
c. In making beverages and fibers.
Thus there are many beneficial bacteria of great importance to humans, animals, and the environment around them.
I edge to this.
It is very informative and has many many points to be noted. thank you so much
a very elaborate one, great job thanks
It is A good essay
It has assisted me to write my assignment