HPLC analysis is one of the types of chromatography used to isolate and analyze mixtures.
HPLC in full form is “High-pressure liquid chromatography.”
Unlike column chromatography, here high pressure is employed in the process. Hence the name.
But also due to its efficiency in the analysis of compounds, it is regarded as High-performance liquid chromatography.
It is derived from column chromatography with enhancements in the separation of components in a short time.
In the column chromatography, the time span required for analysis was too long like few days for a run. Also, the range of compounds that could be analyzed was low and the sample quantity required was high.
In HPLC analysis, a wide range of substances even in minute quantities like in nano-grams or pictograms could be measured at a faster rate.
HPLC chromatography is one of the widely used techniques in the fields like
a. Clinical research,
b. Biochemical research,
c. Industrial quality control, etc.
Applications of HPLC include detection, analysis, determination, quantification, derivation of molecules from mixtures (prep HPLC) of biological, plant and medical importance.
Before going into the details of HPLC theory, principle and further HPLC tutorial, let’s see how it evolved and why?

what is HPLC used for
Before the discovery of chromatography, techniques like gravimetric analysis, photometry, colorimetry (UV, visible detection), titrimetry (acid-base detection), etc.. were sole methods available for analysis. Even the requirements of analysis for research was simple, i.e., there was no necessity for analysis of complex molecules, similar molecules (i.e., molecules with the same chemical and physical properties).
But as research advanced there was the requirement to analyze all the molecules in a given sample for better detection of the problem (in the clinic), impurities and also deficiencies in industry and research.
This was not possible with a single technique like photometric, titrimetric, etc. due to the greater physical and chemical similarity in molecules of a sample like phytoconstituents, amino acids, neurotransmitters, etc..
This posed a problem to analysis, so a combined technique whose estimation is based on physical and chemical properties together was discovered in the form of chromatography. This new method had a significant disadvantage of time required in its process. Sometimes a single sample separation took a couple of days.
With this limitation in mind, further efforts by scientists led to the development of HPLC chromatography with further improvements in speed and efficiency of analysis.
Thus HPLC principle was discovered to analyze like compounds or similar compounds at a faster rate with better efficiency.
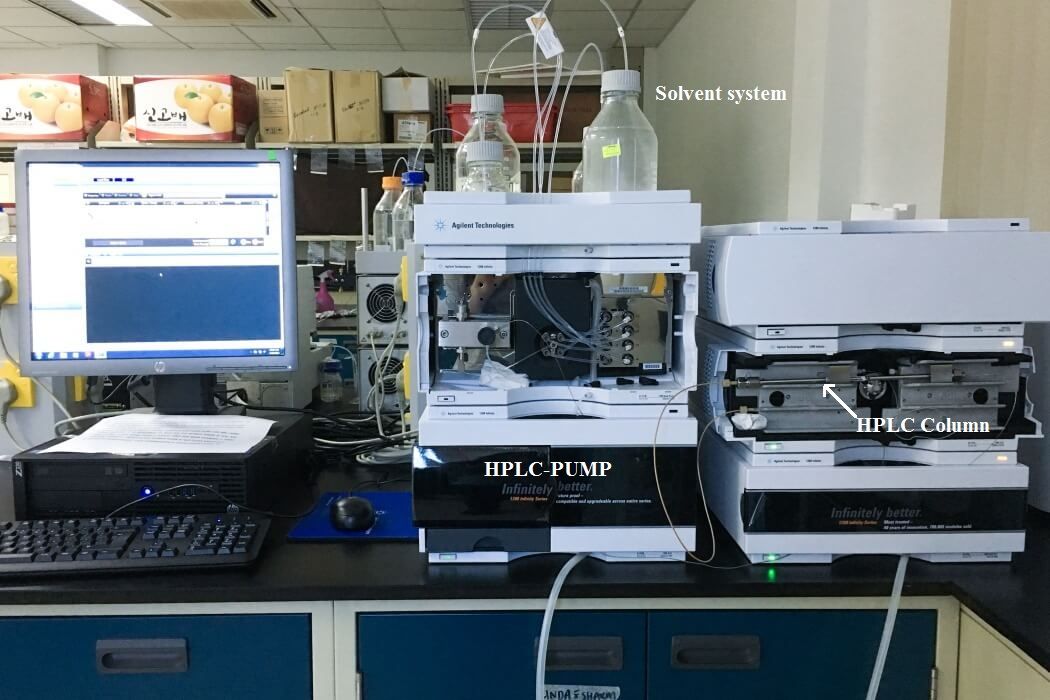
HPLC instrument has an injection system, a pump, column, detectors and a recorder.
HPLC Analysis Principle
The principle involved in HPLC testing is the separation of compounds in a mixture more efficiently and also quickly than that of traditional column chromatography.
Segregation of compounds is due to their relative differences in travel through the column on the application of pressure exerted through the mobile phase or carrying liquid.
The compounds of the mixture travel at different rates due to their relative affinities with the solvent and stationary phase.
Compound with a higher affinity towards the stationary phase of the column moves slowly and vice-versa.
The above principle is similar to that of column chromatography but in HPLC,
The separation is more efficient due to greater surface area achieved due to a tiny particle size of stationary phase in comparison to that used in column chromatography.
This decrease in particle size increases has the disadvantage that it proportionately enhances the flow time and run time due to increased surface area. To minimize this obstacle, the high pressure is applied to the flow of the HPLC mobile phase through the column by use of pumps.
The HPLC procedure is as follows
All the chemicals and reagents used for the process should be of HPLC grade for efficient and smooth analysis.
♦ The mixture required to be evaluated is injected by HPLC injection into a stream of mobile phase which is flowing at a defined pressure.
♦ The injected mixture now does flow over the stationary phase inside the column under the influence of pressure along with the mobile phase.
♦ During this flow based on the affinity of individual compounds in the mixture towards stationary and mobile phase, some compounds get eluted first out of the column and others later.
♦ Outside the column they are sent into a detector where individual compounds are detected and recorded in a computer installed chromatography software.
♦ The recordings (preferably in the form of quantitative peaks) are compared with those of standard compound’s HPLC values, and the individual compounds are identified. So the overall theory of HPLC is relative separation and detection of compounds.
For an overview of the HPLC system and operation see the video tutorial below
♣ Advantages of HPLC:
• It includes both aspects of analysis, i.e., qualitative and quantitative analysis.
• HPLC method evaluates almost all the molecules of the same family.
• For example, in one single run, all the monoamines like dopamine, epinephrine, serotonin can be estimated. A single run for steroids in one sample gives the data of all the steroids in that sample.
• Molecules with small differences in absorption wavelengths can be detected well due to their differences in separation time. I.e., one which travels faster is measured before the other which is measured later. This is the prime advantages if HPLC which makes it non-replaceable.
• Substances in very low concentration like nano and picograms can be detected due to the sensitivity of HPLC detectors used like the electrochemical detector, fluorescence detector, etc.
• Due to its high separation efficiency, the quality of substance obtained by preparative mode or technique (prep HPLC) is of high purity.
♣ Disadvantages of HPLC:
• It’s an expensive method as it requires costly HPLC instrumentation, columns and also uses of the highest grade of purity solvents, buffers, chemicals, etc. termed as HPLC grade.
• Working on HPLC requires heavy processing before estimation like mixing, homogenization, filtration, degassing, derivatization, etc. These techniques are also to be performed with proper care to avoid problems in estimation.
• The systems operation requires prior HPLC training and active HPLC troubleshooting skills. So prior practice is essential to run these chromatography systems.
• HPLC Data obtained is non-homogenous and is never without any noise (fluctuation) and errors during estimation.
• It’s time-consuming, and you must have a good amount of patience.
• Alteration in temperature and presence of dust in chromatography lab can greatly vary the result output. So strict maintenance of experimental conditions is required throughout the process.
This HPLC has many applications in industry and research.
You may also like to read Column chromatography
am glad learning with you since you give detailed and well established notes