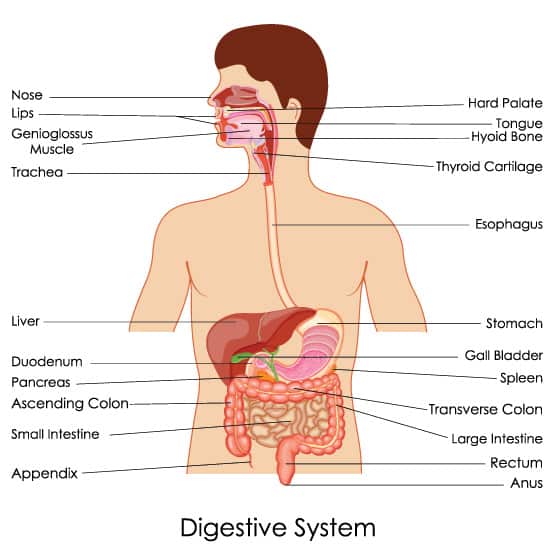
The digestive system is the most essential organ systems that provides strength and energy to the body.
It is the only route through which foreign material, including food, can enter the body directly.
The system is designed to make the foreign substance safe and compatible for the body to absorb.
How does the human digestive system work
The work is the step-by-step process of how the digestive system works like
- Ingestion of food (food intake)
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Propulsion
- Elimination
Ingestion
The food is taken into the digestive system through the mouth.
The process occurs through
- Chewing
- Bolus formation
- Swallowing
Chewing
- It is the mechanical breakdown of food materials by the teeth.
- The teeth break down the food into smaller particles by cutting, tearing, and grinding actions.
- Bolus formation is mixed with saliva simultaneously with the help of tongue and jaw muscles.
- This mixing and chewing lead to the formation of bolus, a small ball-like form ready to swallow.
Swallowing
It involves the movement of the bolus from the mouth into the stomach through the esophagus.
This occurs in 3 processes.
- The mouth is closed, and the tongue and cheek muscles push the bolus backward into the pharynx.
- When the bolus is in the oropharynx, the involuntary action starts, pushing it into the esophagus. During this process, all the routes except for the esophagus route are closed.
- Through a series of peristaltic movements, the bolus in the esophagus is propelled into the stomach.

Propulsion
- This involves mixing food with digestive juices and then the movement of it through the digestive tract.
- This propulsion starts from the time the food is in the esophagus till it is eliminated from the large intestine as feces.
- The role of propulsion is to provide better digestion, efficient absorption, and excretion of waste.
The digestive tract is made up of smooth muscle like.
- Circular,
- Longitudinal, and
- Oblique muscles.
These muscles help churn and squeeze food in the gut.
Due to this action, the food is mixed well with the digestive juices.
Then, the food is moved for better absorption.
The lengthy intestine offers a larger surface area for better absorption of food.
Further, propulsive action moves the undigested food to reach the large intestine.
Digestion
The food is digested by enzymatic action to release glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids.
a) The mechanical crushing of the food by teeth.
- Due to this, larger food particles are broken down into smaller ones.
- As you are aware, the smaller the particle size, the greater the surface area.
- Greater surface area leads to better enzyme action and absorption.
b) Enzymatic digestion of food into smaller molecules like glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids.
- The enzymatic action of food by the digestive juices starts from the buccal cavity and is in the stomach and small intestine.
Digestion in the buccal cavity
The saliva in the mouth helps partially digest food.
- Saliva is produced by the salivary glands has an enzyme amylase.
- This amylase breaks down complex carbohydrates like starch into disaccharides like maltose.
- Hence, one can notice the sweet taste of food when we chew it.
- The pH for this action is between 5.8 to 7.4. This enzyme action continues until the food reaches the stomach.
In the stomach, at a pH of 1.5, the amylase breaks down due to the action of gastric acid.
Digestion in the stomach
- In the stomach, the food is retained for 1 to 2 hours before it is passed into the intestine.
- The food is subjected to sterilization and also partial digestion.
- The hydrochloric acid in the stomach kills the live forms of matter and ensures sterilization.
- Here, the food is mixed with gastric juice,e which contains the enzyme trypsinogen, which is activated by trypsin.
- This trypsin converts proteins to polypeptides.
- Further, some amount of water and alcohol is absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
- Hence, we get rid of thirst immediately after drinking water.
- Even the effects of alcohol intake are observed quickly due to faster gastric absorption.
The acidic content in the stomach converts iron into a soluble form for easy absorption.
Digestion in the intestine
- In the intestine, all food components, like carbs, proteins, and fats, are digested and absorbed.
Intestinal juice released from the pancreas has 5 enzymes like
1. Intestinal amylase: This converts polysaccharides from starch into disaccharides.
2. Trypsinogen: The active form of trypsin Converts polypeptides to tripeptides, dipeptides, and amino acids.
3. Chymotrypsinogen: The active form of chymotrypsin acts on polypeptides similar to trypsin.
4. Lipase: This converts fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
5. Nucleases: Digests DNA and RNA.
Absorption
- The digested food material is absorbed through the small intestines, which are key organs of the digestive system.
- This then reaches the blood circulation through the liver and lymphatic system.
- This absorption occurs due to diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport.
- Monosaccharides, amino acids, water-soluble vitamins, and minerals pass into the capillaries of villi.
- Fatty acids, glycerol, and fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed into the lymphatic system through lacteals.
- Even the large intestine absorbs water, minerals, and vitamins.
Elimination
- The undigested food material is removed from the alimentary canal as feces.
- This is possible due to the peristaltic movement of the intestines.
- These movements force the waste towards the large intestine, sigmoid colon, and rectum.
- From the rectum, due to intra-abdominal pressure, the feces are expelled.
In homeostasis
The digestive system is also involved in maintaining the body’s homeostasis.
The two major physiological variables regulated are
- Blood glucose levels.
- Water and electrolyte levels and
The blood glucose level in the blood should be optimum and maintained by homeostasis.
- When blood glucose levels are low, a feeling of hunger makes a person desire food.
- When the food is consumed, it leads to a sudden release of glucose into the blood from the liver.
- In contrast, when the glucose levels are high, the pancreas releases insulin to decrease blood glucose levels.
- When water levels and electrolyte levels are low, there is thirst, and a person tends to drink water.
In doing so, the water and electrolyte levels are raised.
Frequently asked questions and answers.
How do the digestive system and circulatory system work together
The digestive system helps absorb nutrients from food and passes them into the circulatory system. The circulatory system then distributes the nutrients to the whole body’s tissues.
Further, the circulatory system carries water-insoluble material back to the digestive system and helps expel it through feces.
How does the digestive system help the body maintain homeostasis?
Blood glucose levels and
Water and electrolyte concentrations
These are the two physiological variables in which the digestive system is involved.
Are teeth part of the digestive system?
Yes, teeth are specifically meant to aid the digestive system and are part of it as they are located in the buccal cavity and entry point of the digestive tract.
They help mince the food for easy digestion and absorption.
this is very helpful for my science project, thank you!
Hi, dawn, glad to know that you found it helpful.