Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) are the energy molecules of our body.
Of them, ATP is the essential link between the energy-consuming and energy-producing functions of the body.
Hence, ATP is called the body’s energy currency.
However, both ATP and ADP are similar in some ways.
How Are ATP And ADP Related?
- Both are specifically meant for the Energy process in the body
- Chemically, they have the same set of atoms
- They are constantly formed and destroyed in the living body
- They are metabolized by hydrolysis reaction.
- Equally distributed in the body.
Involvement in the Energy process
- Both ATP and ADP are involved in the energy processes of our body. They release energy when their phosphate bond is broken.
- Approximately 7300 calories per mole of ATP is released from each bond, and the same bond releases around 12,000 calories inside the body.
- The ATP breaks down to ADP and releases energy when energy is needed.
- Immediately, ADP is converted to ATP to replenish lost stores.
- However, ATP has higher energy levels than ADP as it has 3 bonds. ADP has low energy comparatively.
When ATP converts directly to AMP, the energy released is 24000 Cal/Mole.
Chemical similarity
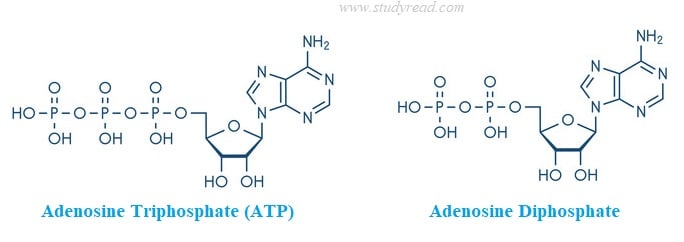
- Chemically, both have adenosine in their structure. This adenosine is a nitrogenous base containing adenine, a five-carbon sugar, ribose and phosphate groups.
- ATP molecule has one phosphate group more than its precursor ADP.
- Both ATP and ADP have one monomer of an adenine nitrogen base and also one carbohydrate monomer, i.e., ribose, a 5-carbon sugar.
- The phosphate groups are present in the α, β, and γ positions. When hydrolyzed, the energy is released due to the removal of the phosphate group on γ position.

- The phosphoanhydride bonds present in these molecules are the reason for high energy generation.
- These bonds are present in both ATP and ADP, where the energy is stored.
Constant formation and destruction in the living body
- Both ATP and ADP are in dynamic equilibrium, which means they are constantly formed and broken down to satisfy the body’s energy needs.
They are metabolized by hydrolysis reaction.
- ATP breaks down to ADP by hydrolysis, which involves adding water.
- Similarly, ADP breaks down to AMP (adenosine monophosphate) when required.
Thus, both molecules undergo hydrolysis as a part of their metabolism in the body.
Equal distribution
- ATP is needed to provide energy for different purposes like synthesis, ion transport, muscle action, nerve conduction, etc.
- So ATP is present in every part of the body. Since it is also broken down into ADP, even ADP is present in all the cells.
They are interchangeable
- With just an addition or removal of a phosphate group, ATP and ADP are interchangeable in structure.
-
Is ATP a nucleic acid
ATP is similar to other nucleic acids like DNA and RNA in structure. But, it is not exclusive to the nucleus like others.
Structurally, like DNA and RNA, which are actual nucleic acids, ATP also has a nuclear base, a ribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
-
What is the structural difference between ATP and ADP
ADP, as seen in the image above, has one phosphate group lesser than ATP
-
Which chemical change will convert ADP to ATP
Phosphorylation converts ADP to ATP and is an endoergic reaction.
-
A high-energy bond in ATP is present between
Two phosphate groups have high energy bonds joining them.
-
Where is energy stored in an ATP molecule
The energy in ATP is stored in the form of phosphate bonds.
-
Which has more potential energy, ATP or ADP?
ATP definitely has more potential energy than ADP.
-
Does ATP have ribose or deoxyribose
ATP and ADP both have ribose as a sugar moiety.