Bacteria release substances that are harmful to the host. These are exotoxins and endotoxins.
Exotoxins are toxic substances that are secreted by bacteria outside of their cell. While the endotoxins are toxins located within the cell membrane.
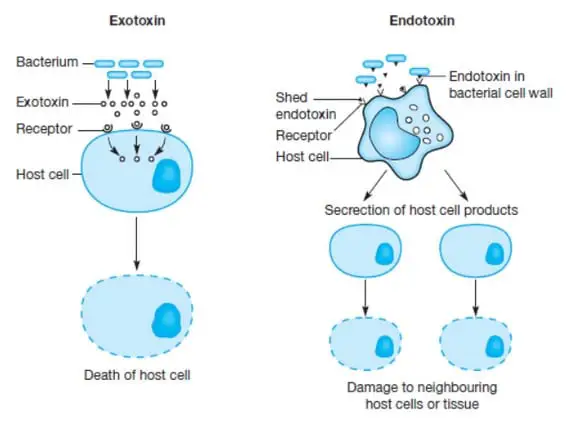
Exotoxin Vs Endotoxin
| Sl.NO | Characteristics | Exotoxins | Endotoxins |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Source | Produced from the live gram- positive and gram-negative bacteria. | They are formed only in gram-negative bacteria. Further, they are secreted during the growth and death of bacteria. |
| 2 | Location | Mostly secreted outside the living cell | Present in the outer plasma membrane |
| 3 | Chemistry | Has Protein, with two components (A and B). | Made of lipopolysaccharide complex on the outer membrane |
| 4 | Molecular Weight | 10 KDa. | 50-1000 kDa. |
| 5 | Isolation | Filterable | Partially filterable. |
| 6 | Genetic link | Frequently carried by extra-chromosomal genes such as plasmids. | They are synthesized directly by chromosomal genes. |
| 7 | Types | Based on their structural and physiological properties, these are classified as. 1) AB Exotoxin 2) Specific host site Exotoxin 3) Membrane Disrupting-Exotoxin a) Channel-forming b) Phospholipase exotoxin 4) Superantigen | Nil |
| 8 | Bacterial Examples | Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes. | E.coli, Salmonella typhi, Shigella, Vibrio cholera. |
| 9 | Diseases caused | Botulism, Diphtheria, tetanus | Gram-negative infections, Meningococcemia. |
| 10 | Symptoms | No Feverish symptoms | High-temperature fever due to the release of interleukin-1. |
| 11 | Toxicity | Highly toxic and even fatal in microgram quantities | Moderate toxicity. |
| 12 | Toxoid Production | Toxins get converted to antigenic, nontoxic toxoids. | Not converted to toxoids |
| 13 | Denaturation | Are easily denatured by boiling. (Sterilization) | Do not get denatured. |
| 14 | Enzyme Activity | No enzymatic activity. | High enzymatic activity |
| 15 | Antigenicity | Exotoxins have high antigenicity. | Endotoxins have poor antigenicity. |
| 16 | Specificity | Specific to a particular Strain. | Nonspecific. |
| 17 | Host Receptors for entry | Exotoxins usually enter host cells through specific receptors. | No specific receptors for the entry of endotoxins. |
| 18 | Antigenicity | Exotoxins have high antigenicity. That is they can evoke a strong immune response in the host. | Endotoxins have poor antigenicity. |
| 19 | Immune Specificity | Specific to a particular Strain | Nonspecific. |
| 20 | Immune Neutralization | Because of a strong immune response, they can be neutralized by antibodies | They are not neutralized by antibodies. |
| 21 | Vaccines | Effective vaccines are available against exotoxins. | No effective vaccines are available against endotoxins. |
| 22 | Role in Disease | Exotoxins affect a human host in three main ways: 1) Ingestion of exotoxin 2) Colonization of mucosal surface 3) Colonization of a wound or abscess. | Endotoxins mediate toxicity in the host through interleukins and Tumor Necrosis factors. |
| 23 | Effect on Host | Highly variable between different toxins. | Similar to all endotoxins. |
| 24 | Enzyme Activity | No enzymatic activity. | High enzymatic activity. |
| 25 | Enzymes | Collagenase, hyaluronidase, nuclease, protease, neuraminidase, phospholipase A. | Catalase, IgA/IgG proteases, fibrinolysin. |
number 21 above – should this read "no effective vaccines are available against" endotoxins rather than exotoxins?
Hi Tony, you are right. We did update the article.