Organic compounds are those compounds which have an element carbon in them.
Their chemistry and reactions are unique to other chemicals.
Some of them are naturally available while others are synthesized by man.
Unlike inorganic compounds, there are some thousands of organic compounds in the current day.
Due to the vastness of compounds, peculiar chemistry, and properties, they are studied as a separate branch i.e. organic chemistry.
These compounds are of different types with different nature and phases.
Also, some of them exist as biomolecules in living beings while others available in nature.
Organic compounds contain mostly carbon, hydrogen and oxygen elements.
Please refer more details on organic chemistry for a better idea.
Examples of organic compounds
Solids: Diamond, coal, graphite, acids like (acetic acid, acetic acid), sugars, fats, etc.
Liquids: Ex: Benzene, pyridine, ethanol, acetylene, etc.
Volatile substances: Naphthalene (shows sublimation).
Gasses: Methane, Acetylene, etc. See types of gases for more.
However the best way to study organic compound examples is with the functional group in mind.
Functional groups are the key structures within the molecule that define the chemical properties of the entire compound.
These are the points of a molecule that undergoes reactions and also contributes to physical properties. The physical nature means the odor, state, and reactivity. So, based on the functional groups, we have different examples as
| Sl.No | Compounds | Functional group | Formula | Uses |
| 1 | Aliphatic compounds | CH | CH3-(CH2)n-CH3. | Ethylene makes polythene covers. Acetylene is used as a gas for welding. |
| 2 | Alicyclic compounds | CH | CH2-(CH2)n-CH2. | Di-ethyl ether is used as an anesthetic. |
| 3 | Ethers | R-O-R | CH3-(CH2)n-O-(CH2)-CH3. | Formaldehyde is used as a disinfectant to preserve biologic samples, etc. |
| 4 | Esters | R-COO-R | CH3-(CH2)-COO-(CH2)-CH3. | All the cooking oils and lipids come under this category. |
| 5 | Aldehyde | R-CHO | CH3-(CH2)n-CHO. | For alcoholic drinks, As solvents, fuel, etc. |
| 6 | Ketones | R-C=O-R | CH3-(CH2)n-C=O-CH3. | Acetone is used To remove nail polish. It is also used as a solvent in chromatography. |
| 7 | Alcohols | R-CH2-OH | CH3-(CH2)n-COH. | For alcoholic drinks, As solvents, fuel, etc. |
| 8 | Amides | R-CONH2 | CH3-(CH2)n-CONH2. | They are part of proteins and are also used in many reactions. |
| 9 | Amines | R-CNH2 | CH3-(CH2)n-CHNH2 | As bases in acid-base titrations, as dyes, as drugs like chlorpheniramine (anti-allergy) |
| 10 | Amino acids | HOOC-CHR-NH2 | HOOC-CH2-NH2 | They are building blocks of proteins. |
| 11 | Sterols (Multi-cyclic structures with functional groups | An example is cholesterol, which is meant for cell membranes and Vitamin-D synthesis. | ||
| 12 | Aromatic compounds | Planar unsaturated ring structures. | Benzene | There are many compounds used as solvents, medicine, catalysts etc. |
Let us see organic compound examples in detail.
- Aliphatic compounds
These are the compounds that have carbon and hydrogen elements in them. The bonds between two carbons can vary as one, two, or even three. These compounds can be enormous like Hexane, a six-carbon chain {CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3}, heptane {CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3}, octane eight-member carbon chain, etc.
Ex: Ethane {H3C-CH3}, Ethene {H2C=CH2}, Acetylene {HC≡CH}.
These compounds are used widely. For example, ethene is used in making plastic bags, i.e., polyethylene covers. Acetylene gas is used in gas welding for joining of metal parts.
2. Alicyclic Compounds
As the name indicates, these compounds are similar to the above but form a ring in their structures.
They are formed by a single bond between two carbon atoms in the chain.
They are named Cyclopentane for five carbon rings, cyclohexane for a six-member ring structure, etc.
Compounds with functional groups.
The same aliphatic compounds can have oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, etc. as part of chemistry.
These chemical points in the molecule are called functional groups. These functional groups impart a distinctive character to the plain aliphatic chain or rings.
Functional groups have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
3. Aldehydes
These have an OH group linked to a carbon atom in the chain. Examples include formaldehyde and acetaldehyde.
Formaldehyde is used to store biological specimens.
They are also found in carbohydrate monomers.
4. Ketones
These are the structures having oxygen linked with a double bond to a carbon atom, i.e., {C=O} in the molecule.
Some examples include acetone, glucose, sucrose, fructose, etc.
Acetone is used as a solvent.
While Fructose and other sugars are used as food sources for carbohydrates.
5. Alcohols
Alcohols are those molecules having -OH moiety linked to carbon atoms directly.
There are many types of alcohols based on the molecular size. They are used as solvents due to their high polarity.
However, not all of them can be used due to volatility issues.
Ethyl alcohol, methyl alcohol, and propyl alcohol are widely used due to their volatility and solubility properties.
Also, ethanol is widely used for alcoholic beverages and even as a disinfectant to kill microbes.
6. Esters
These are the molecules that form oils and fats. Examples include Arachis oil, sesame oil, mustard oil, etc.
They have long chemical structures and are susceptible to oxidation when kept open for air for long periods.
Some of them are used as cooking oil, for massage, etc.
7. Ethers
They are compounds with a profuse odor. Hence, they are named ethers.
They have an oxygen atom linked to two carbon atoms. Ex: Diethyl ether (used as an anesthetic).
8. Fatty acids
When esters break down, they release fatty acids and alcohols. They have -COOH structure in their molecules.
Ex: lauric acid, arachidonic acid, etc. These fatty acids are used to make soaps.
9. Amides
These are the compounds formed by the reaction of acids and amines. Amides form substances like proteins, silk, and even drugs like paracetamol.
10. Amines
These are basic in nature and have an ammonia moiety.
Examples: codeine used for cough treatment. They are used as dyes to impart color to drugs, indicators in titration, etc. Ex: sunset yellow, methyl orange.
11. Amino acids
These structures have both carboxylic and amine moiety.
There are many amino acids in the body. They help in the maintenance of the body through the formation of proteins.
Check out for more Organic chemistry for dummies.
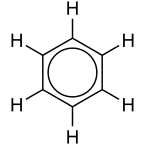
12. Aromatic compounds
These compounds are cyclic but are unsaturated.
They have an odor of their own. Ex: Benzene used as a solvent.
13. Steroid structures.
These structures are quite complex, as seen in the diagram above. They form cholesterol and other structures.
They are derived from fats and lipids. They are used as body boosters drugs. Ex: betamethasone.
14. Organic acids: Perchloric acid (HClO4), citric acid, tartaric acid. Unlike inorganic acids, which are liquids, these acids are in the solid state. They are also not as strong as inorganic acids.
15. Alkyl halides: These are the ones that have halogens in their chemistry. Examples: Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
Functional groups of organic compounds can be determined by specific chemical tests. These tests help to know the nature of the unknown compound in the lab.
Also, read Best Way to Study Organic Chemistry.




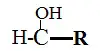


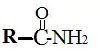
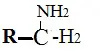
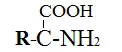

I enjoyed this lesson very much and need more information on this topic.
You Beautifully described about organic compounds
Minerals is an inorganic body found in the earth;ore_pertaining to minerals.
Its has also benifits,the miners collecting minerals,to get an ore.
Minerals is a substance which can be found on earth.