Metabolic pathways are the step-by-step biochemical reactions involved in the synthesis or breakdown of substances in living beings.
These pathways occur in plants, animals, and also in microorganisms.
They occur in almost every cell of the body, and few organs are distinctly meant to be used for these pathways.
In animals, the liver is the critical organ for metabolism. On the other hand, in plants, leaves are organs with high metabolic activity.
Metabolic pathways exist from birth to death of any living organism.
Examples of Metabolic Pathways
1. Respiration
2. Photosynthesis
3. DNA synthesis
4. RNA synthesis
5. Protein synthesis
6. Glycogenesis
7. Glycogenolysis
8. Gluconeogenesis
9. Mevalonic acid pathway
10. Sedoheptulose pathway
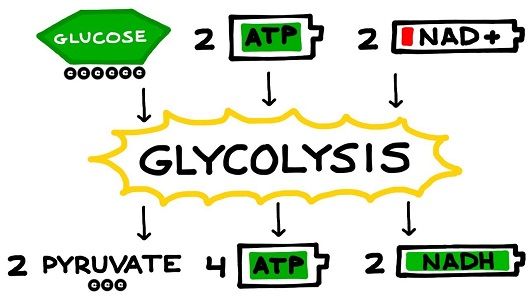
Respiratory pathway:
- This pathway is present in almost all living beings as it generates essential life energy in the form of ATP.
- In most cases, this is an aerobic pathway, which means it happens in the presence of air, i.e., by the use of oxygen gas.
- In the absence of air, few organisms and cells can perform anaerobic respiration for a short time.
- Here, glucose is broken down into lactic acid, thereby releasing the required ATP as energy.
- However, the difference is that aerobic respiration releases more energy per carbohydrate metabolized amount than anaerobic respiration.
- This pathway occurs mainly in the mitochondria of cells.
This pathway has other pathways within it, like
- Glycolysis
- Pyruvate pathway
- Tricarboxylic acid cycle(TCA cycle) or CREB cycle.
Photosynthesis:
- This is the pathway that contributes to the production of food for all the animals on the earth.
- This pathway occurs primarily in plants and a few microbes like Euglena, algae, etc. In plants, this pathway occurs in the leaves.
- The light energy from the sun is trapped in the greenish pigment, namely chlorophyll, in the leaves and used to form carbohydrates.
- This is an anabolic reaction wherein carbon dioxide and water are combined to form glucose-like larger molecules.
- The energy is entrapped in the bonds of carbohydrates. These, when subjected to the respiratory pathway, break down to release energy.
DNA synthesis:
- This pathway is a multifaceted one. First, purines and pyrimidines are synthesized, and sedoheptulose pathways synthesize ribose sugars.
- Once the bases and sugar are ready, DNA undergoes replication to form a new set of DNA using the bases and sugars.
RNA synthesis:
- In scientific terms, it is also called transcription.
- Here, mRNA (messenger RNA) is formed from DNA.
- This RNA is used for protein synthesis.
Protein synthesis:
- This pathway is called translation. Here, amino acids chains are formed on the surface of mRNA.
- These amino-acid chains further polymerize and aggregate to form proteins.
Glycogenesis:
- This is a process of conversion of glucose into glycogen in the presence of insulin.
- This occurs predominantly in the lever, and formed glycogen is stored there for future use.
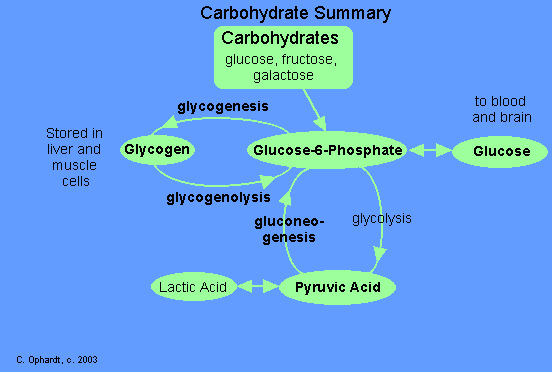
Glycogenolysis:
- Here, the formed glycogen in the lever is broken down to release glucose in times of starvation and need.
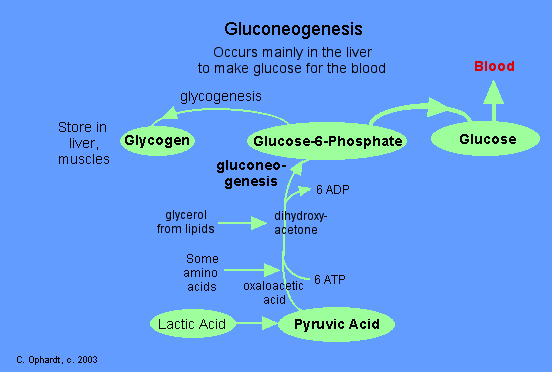
Gluconeogenesis:
- This pathway is one where glucose is synthesized from noncarbohydrate sources like proteins, amino acids, and lipids.
- This predominantly occurs in case of starvation. Hence, the body mass goes down due to starvation as the protein and fat stored in the body are used up to make glucose.
Mevalonic acid pathway:
- This pathway produces five-member carbon molecules, namely isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, which are used to synthesize cholesterol, vitamin K, steroid hormones, etc.

Sedoheptulose pathway:
- This is a pathway wherein seven-carbon sugars, namely sedoheptulose, are formed.
- From this sedoheptulose, ribose sugars required for DNA and RNA synthesis are obtained.