Dopamine and serotonin are both neurotransmitters in the nervous system. They play an important role in the behavior and body physiology.
But they differ from each other in many aspects, like
- Their Chemistry
- Physiological role
- Psychological effects
- Role in diseases
- Metabolism, etc.,
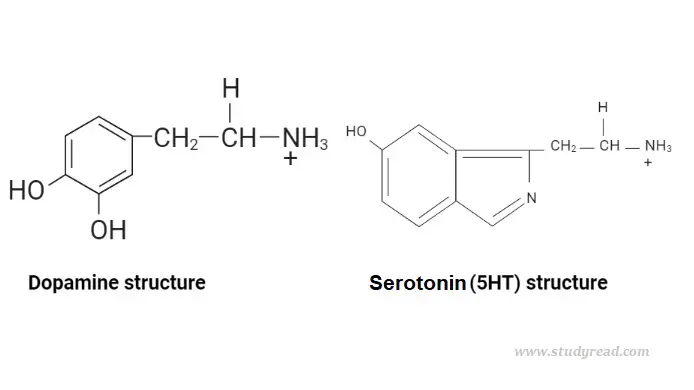
Differences between Dopamine and Serotonin
| Sr.No | Feature | Dopamine | Serotonin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Functions | As a neurotransmitter | It acts as a neurotransmitter and a hormone. |
| 2 | Chemical structure | From neurons originating in the substantia nigra | There are 4 receptors D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5. |
| 3 | Synthesis | It is synthesized from the amino acid phenylalanine. | It is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan. |
| 4 | Secretion in brain | It is mostly located in the brain and, to some extent, in the blood vessels, kidneys, paracrine cells, etc. | By nuclei that originate in the median raphe of the brain stem. |
| 5 | Location in body | Serotonin regulates the secretion of dopamine, besides other neurotransmitters. | Almost 90% of it is located in the enterochromaffin cells of the digestive system. |
| 6 | Metabolism enzymes | It is metabolized by both COMT and MAO enzymes and also aldehyde dehydrogenase. | Both COMT and MAO enzymes metabolize it and also aldehyde dehydrogenase. |
| 7 | Receptors | There are 4 receptors; D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5. | There are 14 receptors like 5HT1 as (1A,1B,1D), 5HT2 as (2A,2B,2C), 5HT3, 5HT4, 5HT5, 5HT6, 5HT7. |
| 8 | Autoreceptor | D2 receptor inhibits the release of dopamine | 5-HT1A receptor inhibits the release of serotonin |
| 9 | Regulation | Dopamine secretion is stimulated by stress and the HPA axis. | Vitamin D and tryptophan regulate the synthesis of Serotonin. |
| 10 | Mechanisms | It has an inhibitory effect in the basal ganglia, while in other brain areas, it has an excitatory effect. | It is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. |
| 11 | Effect on the nervous system | It influences pleasure, causes addiction | Like depression, anxiety, psychosis, irritable bowel syndrome, and autism. |
| 12 | On physiology | It has effects on body movements, lactation | It affects almost the whole body. It influences eating, digestion, sleeping, bowel movements, excretion, coagulation, wound healing, etc. |
| 13 | Role in diseases like | It stabilizes mood, and happiness enhances communication in the nervous system. | It has a role in Parkinson’s disease, psychosis, drug addiction, and anxiety. |