The Difference Between Bacterial cell and Human Cell are few but are quite significant.
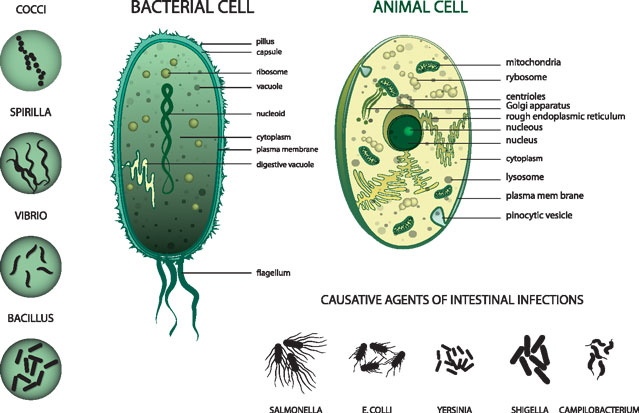
Difference Between Bacterial Cell and Human Cell
| Differences in | Bacterial cell | Human cell |
| Cell | The cell is isolated and Independent. It survives as an individual on its own. | Human cells are in a group and not isolated. It is dependent on other cells for survival. |
| Cell wall | A thick protective cell wall is present covering the whole cell. | The wall is absent |
| The cell membrane is made of | Is made of a phospholipid bilayer. But the membrane lacks sterols. | Lipid bi-layer with phosphate molecules. It is hydrophilic to external and hydrophobic in the inner wall. |
| Cell membrane has | No cytoplasmic bridges as there is only one cell. | Cytoplasmic bridges are present, which help in inter-cellular transport between neighboring cells. |
| Cell shape | Cells can be of different shapes | Only spherical or oval |
| Cell appendages (External parts) | Present. Flagella for movement, pili for sexual reproduction. | Absent mostly. Except for ciliated cells in the respiratory tract & gut. |
| Nucleus | The nucleus is Absent. Instead, nuclear content like DNA is present in the cytoplasm. No distinct nucleus, so-called prokaryote | Prominent nucleus with the nuclear membrane. So-called a eukaryote type. |
| DNA synthesis & Elongation | Enzyme DNA Gyrase is involved. | Enzyme Topoisomerase is involved |
| RNA (ribonucleic acid) | 70s type with the 50s and 30s type subunits. | 80s type with the 60s and 40s subunits. |
| Capsule (a form of an inactive cell) | The bacterial cell undergoes to form a capsule that is resistant to harsh conditions of drought and temperature. Can give back live bacteria in good conditions. | Absent |
| Cell death | The bacterial cell is immortal. It never dies unless subjected to sterilization. Divides for new offspring. Even in harsh conditions, it tries to survive as spore form (dormant) | The human cell is mortal. The cell dies by either apoptosis or necrosis. |
| Nutrition | Autotrophic, heterotrophic, parasitic, etc. Autotrophs manufacture their own food. Disease-causing bacteria are parasites & live on other organisms. | Heterotrophs. Depends on the food supplied by blood from the body’s gut. |
| Reproduction | Both sexual and asexual reproduction happens | Asexual reproduction only. |
| Cell division occurs by | Mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis gives two cells, and meiosis gives fur cells | All cells undergo mitosis. Only ovum and sperm formation by meiosis. While nerve cells never divide. |
| Movement | They can move on their own with flagella for normal needs. | Cannot move, except for sperm and ova. At the same time, blood cells flow in the fluid. |
Before you go into details, kindly check the details on the cell and its organelles.
Also, there are variations like the bacteria are immortal creatures, i.e., they do not die as such except under harsh conditions.
They are quite primitive living organisms on the earth and are of various types. On the other hand, a human is an advanced living being.
As you might have heard before, they cause various diseases in humans. But there are also friendly and useful bacteria.
They are single-celled organisms, and yet that single cell can perform all of its functions.
These differences are the key to the treatment of bacterial diseases by the use of antibiotics.

It would be difficult to target and kill bacterial cells without such differences once they get into the human body.

- The difference between a bacterial cell and a human cell helps us fight bacterial infections.
- When administered into the human body, antibiotics act in such a way that only bacterial cells are killed while sparing humans.
- The common targets to achieve this safe drug action are the cell wall, 70s ribosomes, DNA gyrases, etc.
Ex: Penicillins kills bacteria by acting on their cell wall.
- Since human cell lacks a cell wall, human cells are not affected by it.
- Similarly, streptomycin acts only on 70s ribosomes and prevents their protein synthesis, while there are 80s ribosomes in human cells.
- So they are not affected by the antibiotics.
You may Also Like the Differences between cell membrane & Cell Wall.
- Besides, the translation of a process involved in the formation of a new protein from mRNA is entirely different in bacteria.
- In humans, the m-RNA formed by transcription comes out of the nucleus and then translation over the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- But in bacteria, there is no nuclear membrane.
- So the formation of mRNA and the formation of protein synthesis happen almost simultaneously.
helpful to me thanks for that
hope to email me more information to my email add. thank u!