Blood is the liquid connective tissue and is part of the body’s circulatory system.
This blood acts as a transport medium and performs many essential activities.
The blood components can be broadly classified into a
- The cellular fraction makes up to 45 % and
- Plasma comprises 55%.
Chemical Composition of Blood
Blood has two parts
1. Blood cells
- Red blood cells
- White blood cells
- Platelets or thrombocytes
2. Plasma

Blood cells
- This portion forms 40% of the total blood and has formed elements called cells.
- These cells are all formed in the bone marrow and released into the bloodstream.
Red blood cells
- These cells are called red blood corpuscles or erythrocytes.
- The blood is red in color due to the presence of these cells in large concentrations.
- They have hemoglobin in their matrix and help in carrying oxygen from the lungs to the tissues.
Read more on Red Blood Cells on a separate page
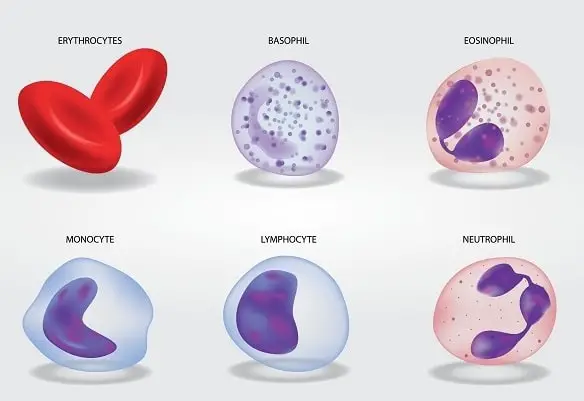
White blood cells
These cells are white in color and are of five types:
- Neutrophils
- Acidophils
- Basophils
- Monocytes and
- lymphocytes.
These white blood cells help to combat infections and help prevent infectious diseases. For more details, refer to the types of white blood cells.
Thrombocytes
These cells are also called platelets. These cells are involved in hemostasis.
Plasma
This is the clear, straw-colored fluid portion of the blood.
It makes up 55% of the blood volume.
It has up to 90% water and 10% soluble and suspended materials. The solid material includes
- Proteins like albumin and globulin.
- Nutrients
- Gases (Oxygen, carbon dioxide)
- Waste material
- Lipids
- Electrolytes like Na+, Ca+
- Hormones
- Enzymes
Proteins
- Plasma proteins constitute 7% of the plasma volume.
- These include serum albumin, globulin, and immunoglobulins.
- These proteins are large and hence unfiltered through capillaries into the kidney glomerulus.
- Hence, these proteins are retained in the blood and contribute to the osmotic pressure of the blood.
- Due to this osmotic pressure, the blood stays within the blood vessels.
Albumin
- This albumin constitutes 60% of total plasma proteins.
- The serum albumin binds with water, cations, hormones, free fatty acids, steroidal hormones and drugs.
Globulins
The globulins are plasma proteins that are of the following types like
- Alpha 1 globulins
- Alpha 2 globulins
- Beta globulins
- Gamma globulins
- These globulins help maintain colloid osmotic pressure
The gamma globulin help produces the immunoglobulins to provide immunity against microbes and foreign antigens.
- While thyroglobulin carries thyroxine hormone and transferrin carries iron.
Fibrinogen
- This is a major clotting factor and helps in the coagulation of blood (hemostasis).
- They prevent the formation of blood clots in the circulation, leading to the blockage of small vessels.
Albumin and fibrinogen contribute to blood viscosity.
Nutrients
- Blood carries nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids from the digestive system to other tissues.
- Glucose is meant for energy generation in the form of ATP. Amino acids are used as building blocks for protein synthesis.
Gases (Oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen)
- nThe gases oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen, are present in the plasma.
- Oxygen is supplied from the lungs to the tissue. CO2 is carried from tissues to the lungs for expiration.
Waste material
- Waste material is carried from the tissues to the kidney for excretion.
- These include urea, uric acid, ammonia, creatinine, lactic acid, bilirubin, etc.
Lipids
Lipids like HDL, LDL, and VLDL are present in the blood.
Electrolytes
- Plasma has many electrolytes of Na, Ca, K, Mg, Fe, PO, etc.
- These help in the proper transmission of nerve impulses and maintain the pH of the blood by acid-base balance.
- The blood pH is slightly alkaline and is around 7.35 to 7.45.
Hormones
- Hormones are substances released from the endocrine glands.
- These are carried away to the tissue.
- Enzymes SGPT, SGOT, etc., are present in the plasma.
Frequently asked questions and answers
Plasma proteins essential in body defense are the
Globulins are the plasma proteins essential in antibody formation and body defense against microbes and foreign cells.
The combination of plasma and formed elements is called
Blood is the combination of plasma and formed elements.
Why is the blood a tissue and not a cell or organ?
Blood is a made of 3 different types of cells. So it is a tissue and not a cell.
Each of the cells types in blood have their own functions so, blood is not an organ meant for one specific type of function.